What Is tDCS Treatment and How Does It Work for PTSD?

Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a mental health condition that can develop after a person has experienced or witnessed a traumatic event. Individuals with PTSD may suffer from flashbacks, anxiety, nightmares, and intrusive thoughts that can interfere with their ability to function in daily life. While traditional treatments such as therapy and medication can be helpful, many people with PTSD seek alternative therapies. One such option gaining attention in Australia is Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS) treatment. In this post, we’ll explore what tDCS is and how it works as a potential treatment for PTSD.
What is tDCS Treatment?
Understanding tDCS
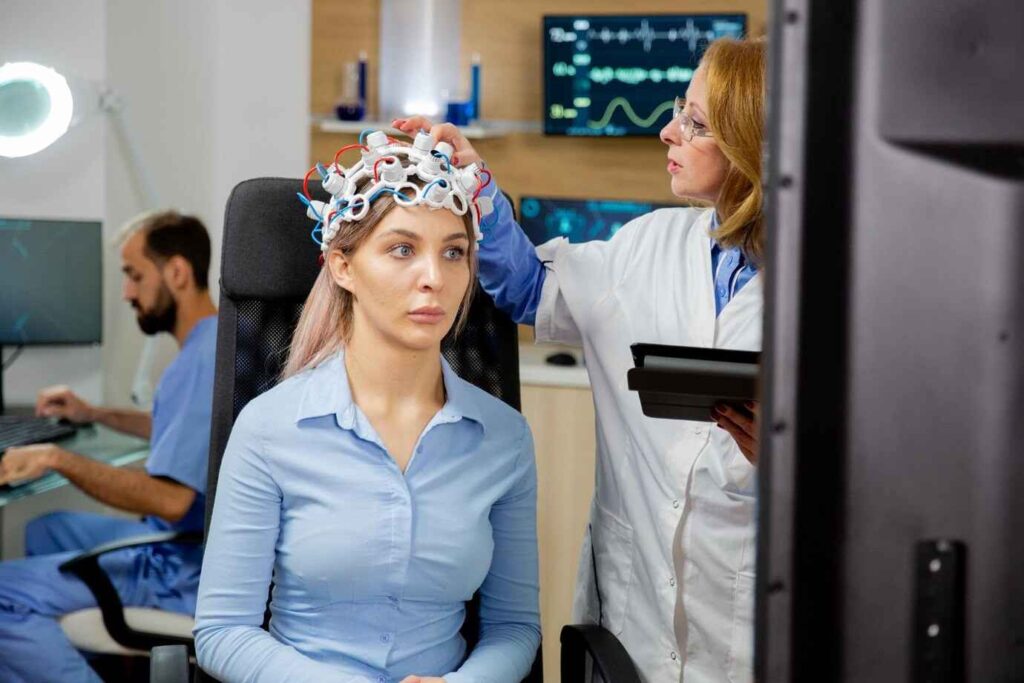
Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS) is a non-invasive brain stimulation therapy that uses a low electrical current to modulate brain activity. By placing small electrodes on the scalp, a mild electrical current is delivered to specific areas of the brain. This stimulation can either enhance or inhibit neural activity, depending on the area being targeted. The goal is to alter the brain’s functioning in a way that improves mood, cognitive function, and emotional regulation.
The Science Behind tDCS
tDCS works by influencing the electrical activity of neurons in specific regions of the brain. The current does not directly stimulate the neurons but rather alters their level of excitability, making them more or less responsive to other stimuli. This can result in changes in how the brain processes information, which can have therapeutic effects for various mental health conditions, including PTSD.
In the case of PTSD, research suggests that tDCS may help regulate areas of the brain that are involved in emotional regulation and memory processing, areas that are often affected in individuals with PTSD.
How Does tDCS Work for PTSD?
Targeting Key Brain Areas
PTSD is often associated with abnormal activity in specific areas of the brain, including the prefrontal cortex (PFC) and the amygdala. The PFC is responsible for regulating emotions and decision-making, while the amygdala is involved in the processing of fear and trauma-related memories. In individuals with PTSD, these areas often show heightened or decreased activity, which can lead to the symptoms of the disorder.
tDCS can target these brain areas to help normalise their activity. By stimulating the PFC, tDCS may enhance its ability to regulate emotions and thoughts, helping individuals manage anxiety and intrusive memories. Similarly, modulating the activity of the amygdala can help reduce the intensity of traumatic memories and the emotional responses associated with them.
Reducing Symptoms of PTSD
Through targeted stimulation, tDCS can potentially reduce the intensity of PTSD symptoms. Studies have shown that individuals who undergo tDCS treatment in Australia may experience improvements in mood, anxiety levels, and the frequency of intrusive thoughts. These benefits can help individuals regain control over their emotions and responses to trauma-related cues, leading to a better quality of life.
While tDCS does not cure PTSD, it can serve as a valuable adjunct to other treatments, such as cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT) and medication, by enhancing the brain’s ability to process and regulate emotions.
The Benefits of tDCS Treatment for PTSD in Australia
Non-Invasive and Drug-Free Treatment
One of the key advantages of tDCS is that it is a non-invasive, drug-free treatment option. Unlike medications, which can come with a range of side effects, tDCS uses low-level electrical currents to influence brain activity without the need for pharmaceutical interventions. This makes it an appealing option for individuals who prefer non-medication-based treatments or those who have not responded well to traditional therapies.
Minimal Side Effects
tDCS is generally well-tolerated, and the side effects are minimal. Some individuals may experience mild sensations, such as tingling or itching at the site of the electrodes, but these are typically temporary and resolve quickly after the session. Unlike medications that can cause fatigue, weight gain, or other side effects, tDCS offers a much lower risk of adverse effects.
Customised Treatment for Individual Needs
tDCS treatments are highly individualised. The placement of electrodes and the intensity of the electrical current can be adjusted based on the patient’s unique needs and response to treatment. This flexibility allows for a more tailored approach, ensuring the therapy is effective for each person.
Convenient and Short Sessions
Each tDCS session typically lasts between 20 to 30 minutes, making it a relatively quick and convenient treatment option. For individuals with PTSD, who may already be dealing with the challenges of managing their symptoms, this time-efficient treatment can fit easily into their schedules. Sessions are typically done in a clinical setting, although portable devices are also available for home use under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
How to Access tDCS Treatment in Australia
Finding a tDCS Provider
In Australia, tDCS treatment is available through certain mental health clinics, hospitals, and private practitioners who specialise in brain stimulation therapies. It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider who is trained in tDCS and understands its use in the treatment of PTSD. Your doctor or mental health professional can guide you in finding a reputable clinic or specialist offering this service.
Combining tDCS with Other PTSD Treatments
While tDCS can offer significant benefits, it’s often most effective when used in conjunction with other treatments for PTSD, such as psychotherapy or medication. Cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT) and exposure therapy, for example, can help individuals process traumatic memories and develop healthier coping strategies, while tDCS can help regulate the brain’s response to these memories.
Assessing Effectiveness
As with any treatment, the effectiveness of tDCS for PTSD varies from person to person. Some individuals may experience significant improvements in their symptoms, while others may have a more modest response. Ongoing evaluation and monitoring by a healthcare provider can help assess the effectiveness of tDCS and determine whether adjustments to the treatment plan are needed.
Conclusion
Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS) is an innovative, non-invasive treatment that holds promise for individuals living with PTSD. By targeting specific areas of the brain involved in emotional regulation and memory processing, tDCS can help reduce symptoms of PTSD and improve overall mental health. In Australia, tDCS treatment offers a drug-free and well-tolerated alternative for individuals who have not responded to traditional therapies. If you or someone you know is struggling with PTSD, consider consulting with a mental health professional to explore whether tDCS could be a suitable part of a comprehensive treatment plan.